Code Features¶
The main functions available in the preparenovonix package are listed below in alphabetical order. The list contains the module name followed by the function name with the expected input parameters in brackets.
novonix_add.create_reduced_protocol(infile,verbose=False): Given a cleaned Novonix data file,infile, generate a reduced protocol.novonix_add.novonix_add_loopnr(infile,verbose=False): Given a cleaned Novonix data file,infile, add a reduced protocol to the header and the columns Protocol line and Loop number.novonix_add.novonix_add_state(infile,verbose=False): Given a cleaned Novonix data file,infile, add the State column.novonix_clean.cleannovonix(infile): Given a Novonix data file,infile, clean it as it is described below.novonix_io.isnovonix(infile): Given a file,infile, check if it is or not a Novonix data file.novonix_io.read_column(infile,column_name,outtype=’float’): Given a column name,column_name, read it from a cleaned Novonix data file,infile, as a numpy array of the type given inouttype.novonix_prep.prepare_novonix(infile,addstate=False,lprotocol=False,overwrite=False,verbose=False): Master function of thepreparenovonixpackage that prepares a Novonix data file by cleaning it and adding to it derived information. This function follows the flow chart presented in Flow chart. Running all the available features from the preparenovonix package through this function can take form few seconds to up to few minutes depending on the size of the input file.
In what follows, the above functions will be referred by simply their name, without stating the modules they belong to.
Flow chart¶
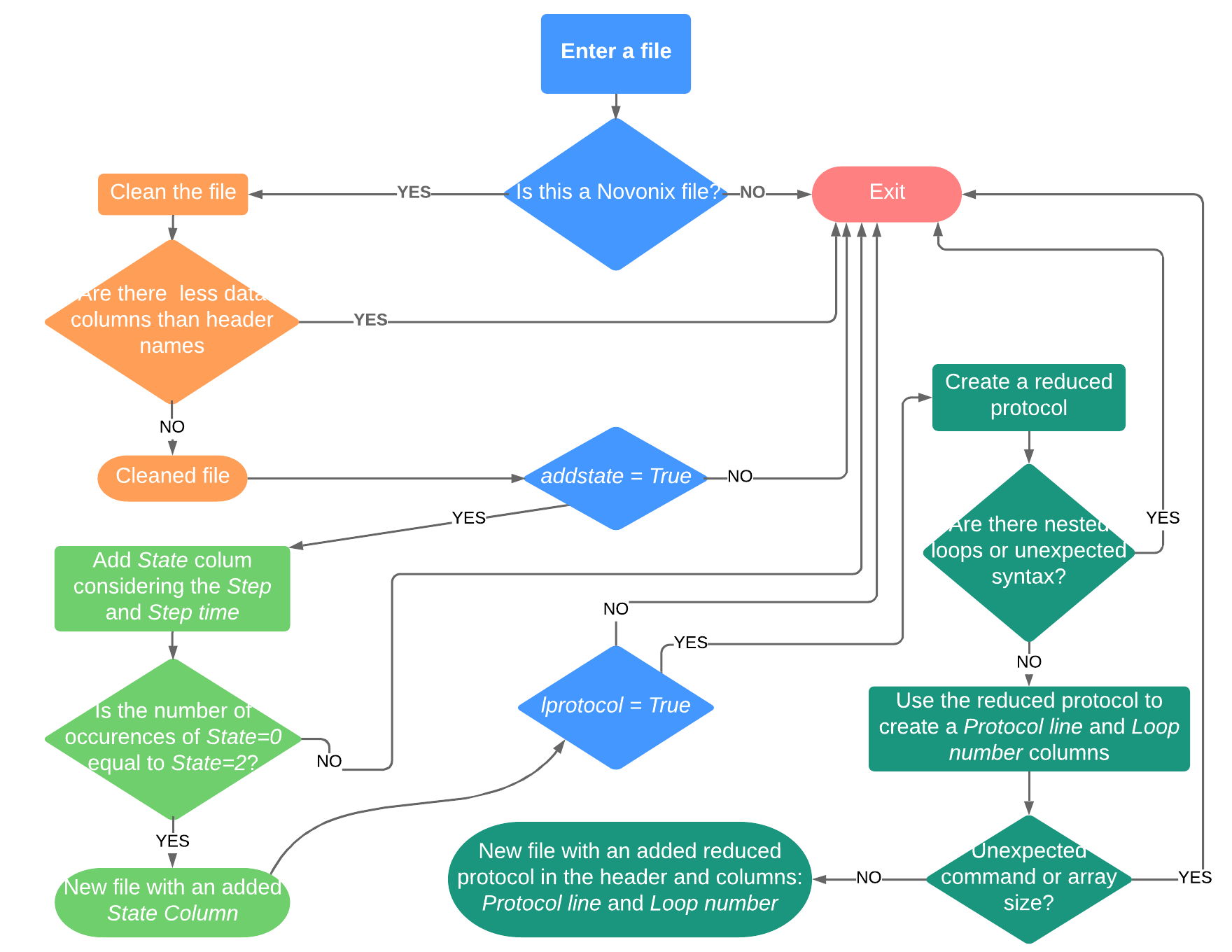
Flow chart for the prepare_novonix function (within the
novonix_prep module) which contains all the functionality of the
preparenovonix package presented here. Besides the name of the input
file, this function has four optional boolean input parameters:
addstate, lprotocol, overwrite and verbose. The last two
parameters are not included in the flow chart, but they are described in
the text. In this chart rectangle shapes indicate processes, rounder
rectangles end of processes and diamonds decisions. Note that for
simplicity not all the decisions made in the code are shown here.
The prepare_novonix function¶
As it is shown in Flow chart, the preparenovonix package only cleans data files that are consider to
be exported from the Novonix battery-testers and it only derives
information for cleaned Novonix files. The master function prepare_novonix allows the user to
call either the cleaning process or the addition of extra columns
ensuring that these dependencies are taken into account. The input
parameters for this function are the path to a file and four boolean
optional parameters: addstate, lprotocol, overwrite and
verbose. The last parameter provides the option to output more
information about the run. If the overwrite parameter is set to
False, a new file will be generated with a name similar to the input
one, except for the addition of _prep before the extension of the
file.
The isnovonix function¶
The function isnovonix decides if a file has the expected structure (including a full header)
for an exported file produced by the Novonix battery-testers. If the
file is lacking the header or if it has not been exported with a Novonix
battery-tester using the covered software (see the section Compatibility), the code will exit with
an error message and without generating a new file.
The cleannovonix function¶
The function cleannovonix produces a new Novonix type file after performing the following tasks:
- Delete failed tests within a single file, adding the final capacity of all failed tests to the capacity column of the finished test.
- Remove individual measurements for which the run time goes backwards.
- Remove blank lines from the header.
- Remove any trailing characters from the header produced when the file has been previously open with certain programs, such as Excel.
- Add a dummy header name (
dum[number]) for each data column lacking a header name.
The State column¶
A State column can be added to a cleaned Novonix file by calling the function
novonix_add_state or setting to True the parameter addstate
when calling the function prepare_novonix. This State column can
have the following values:
- 0 for the first measurement of a given type (for example, a constant current charge).
- 1 for measurements between the first and last of a given type.
- 2 for the last measurement of a given type.
- -1 for single measurements. This can happen under different circumstances. A type of measurement can end after a single measurement when some experimental conditions are met, this usually happens while the time resolution is coarse. At times, the current can overshoot from negative to positive values at the beginning of a measurement. A bug in the Novonix software that locks certain values, etc. If two single measurements happen together, the two lines are discarded in the new file containing the additional State column.
The State column is generated based on the following quantities provided in the raw Novonix data files: Step number (integer indicating the type of measurement) and Step time (this time is assumed to reset to 0 each time a new type of measurement starts).
The reduced_protocol function¶
The reduced_protocol function reads the complete header from the input file and generates (or reads)
the reduced protocol. This function returns the reduce protocol itself
and a boolean flag, viable_prot. The reduced protocol consist of an
array of strings. Each string contains a line number, a command from the
experimental protocol and the corresponding experimental conditions (if
aplicable); for example: [4 : Repeat 49 times :]. Only commands
referring to the following processes will appear in the reduced
protocol (note that the commands corresponding to incrementing the cycle counter and global emergency limits are ignored in the reduced protocol as there are no measurements associated with those):
- Open circuit storage (or rest)
- Constant current (dis)charge
- Constant current - Constant Voltage (dis)charge
- (End) Repeat
The reduced protocol is tested against the number of unique measurements
in the file, determined using the column State. If the number of
measurements expected from the protocol is less than the actual number
of measurements, the flag viable_prot is set to False,
indicating that the construction of the reduced protocol was not viable.
The Protocol line and Loop number columns¶
The Protocol line and Loop number columns can be generated by either calling directly the function
novonix_add_loopnr or by setting to True the parameter
lprotocol when calling the function prepare_novonix. The column
Protocol line associates a measurment with its corresponding line in the
reduced protocol. The Loop number column has a value of 0 if a
measurement does not correspond to any repetition statement in the
protocol and otherwise it grows monotonically with each repetition (see
Flow chart).
If the flag viable_prot was set to False by the
reduced_protocol function, the Protocol line and Loop number columns
are populated with the value -999.